Pregnancy is a transformative period that brings about various physiological changes. Among these changes is the fluctuation in leptin levels, a hormone predominantly made by adipose cells that helps to regulate energy balance by inhibiting hunger. Understanding how aerobic exercise and antioxidant micronutrients affect leptin levels during pregnancy can provide valuable insights for expectant mothers looking to maintain a healthy lifestyle.
Leptin plays a crucial role in regulating body weight and energy balance, which is particularly important during pregnancy. It helps in modulating the energy requirements of both the mother and the developing fetus. However, imbalances in leptin levels can lead to complications such as gestational diabetes and preeclampsia.
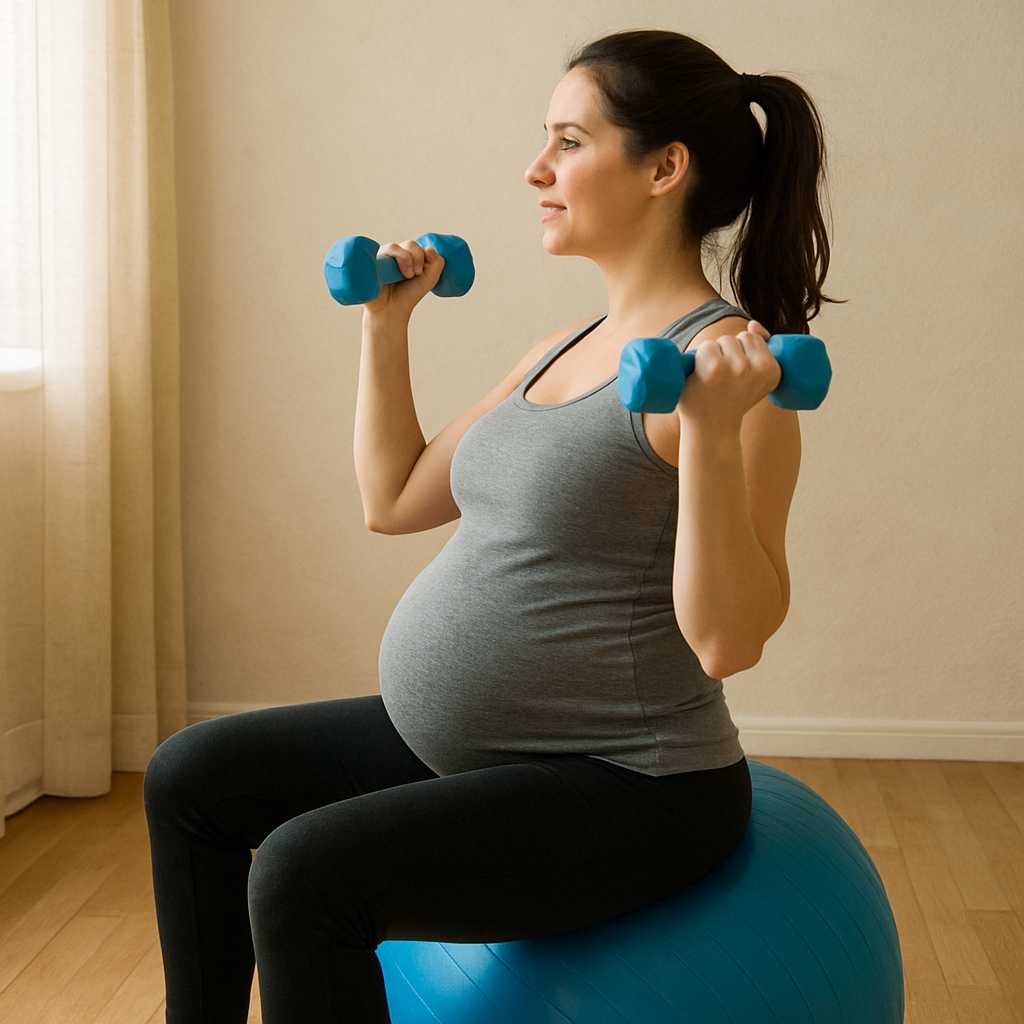
Aerobic Exercise and Leptin Levels
Findings from International Journal of Food Sciences and Nutrition a double-blind randomized controlled trial evaluating the effects of aerobic exercise and antioxidant micronutrient supplementation on leptin levels in healthy pregnant women.
Exercise lowered leptin levels without increases during pregnancy, unlike supplementation. Fat mass and hs-CRP increased in all groups, except for fat mass in the supplementation group. Exercise benefits were independent of fat mass or inflammation, suggesting an alternative mechanism.
Aerobic exercise prevents typical leptin increases, potentially preventing gestational metabolic issues. Supplementation lacks similar benefits and may reduce exercise’s leptin effect.
Exercise effectively manages leptin in healthy pregnancies, unlike supplementation.
Aerobic Exercise During Pregnancy
Regular aerobic exercise is known to improve cardiovascular health and boost overall well-being. But what about its impact on leptin levels during pregnancy?
A recent analysis from a double-blinded randomized controlled trial sheds light on this.
The study found that engaging in moderate aerobic exercise can positively influence leptin levels, helping to maintain a balanced energy environment during pregnancy.
This is beneficial not only for the mother’s health but also for the optimal development of the fetus.
Study supports pregnant women engaging in regular aerobic exercise to optimize metabolic health and provides valuable insight into the limited additive value of antioxidant supplementation in regulating leptin during pregnancy.
Aerobic exercise during pregnancy prevents the typical rise in leptin, possibly offering protective effects against gestational metabolic complications. Antioxidant supplementation does not confer similar benefits and may even attenuate exercise’s effect on leptin.
Alongside aerobic exercise, antioxidant micronutrients play a vital role in managing leptin levels. These nutrients help combat oxidative stress, a natural process that can be heightened during pregnancy. Vitamins such as C and E, along with minerals like selenium, are essential in maintaining a healthy balance of leptin levels.
In conclusion, aerobic exercise prevented leptin elevation during pregnancy, independently of fat mass changes. AMS attenuated this benefit when combined with exercise.